User Administration
What is User Administration in SAP Basis?
To start user maintenance you have to use the transaction code SU01. You can create a new user or copy
the existing user master. The user master contain all data and setting that are
required to log on to a client.
In this you can find the following tabs:
Address: Personal info and address
Logon Data: Password and validity period of the user
User Default: Language, Values for printer
Parameters: User specific values for standard fields
Roles and profiles: Roles and profiles assigned to the
user
Groups: Grouping users for mass maintenance
User Administration in SAP Basis
Types of User
Dialog User, Communication User, System User, Service User, Reference
User.
Description about the above User types:
1. Dialog
For Dialog User GUI Login is possible, Initial password and
expiration of password and Multi GUI Logins are checked.
· Individual system access
(personalized)
· It is possible to log on
using SAP GUI. The user is therefore capable of interaction through SAP GUI.
· The system checks whether
the password has expired or is initial.
· The user can change his or
her password himself or herself.
· Multiple dialog logons are
checked and, where appropriate, logged.
· Purpose of Dialog User is
for individual human users.
2. System:-
For a System User GUI Login is not possible, Initial password
and expiration of password are not checked.
System-related and internal system processes.
It is not possible to log on using SAP GUI. The user is therefore
incapable of interaction through SAP GUI.
The password change requirement does not apply to the passwords, that is,
they cannot be initial or expired.
Only a user administrator can change the password.
Multiple logons are permissible.
Purpose of System User is for background processing and communication
within a system (internal RFC calls) and between multiple systems (external RFC
calls).
3. Communication:-
For a Communication User login is not possible, Users are allowed to
change password through some software in middle tier Individual system
access (personalized)
It is not possible to log on using SAP GUI. The user is therefore
incapable of interaction through SAP GUI.
Although the system checks whether the password has expired or is
initial, the implementation of the requirement to change the password, which
exists in principle, depends on the logon method (interactive or
non-interactive).
Purpose of this User is for external RFC calls of individual human users.
These are used for login to system through external systems like web
application
4. Service:-
For a Service User GUI login is possible. Initial password and expiration
of password are not checked. Multiple logins are allowed. Users are not allowed
to change the password. Only admin can change the password.
Shared system access for a larger, anonymous group of users. Assign only
very restricted authorizations for this user type.
Purpose of this User is for anonymous users. This type of users should be
given minimum authorization. After an individual authentication, an
anonymous session begun with a service user can be continued as a
person-related session with a dialog user.
5. Reference:-
For a Reference User GUI login is not possible. Initial
password and expiration of password are not checked. User type for general,
non-person related users that allows the assignment of additional identical
authorizations, such as for Internet users created with transactions SU01.
Purpose of this Users are special kind of users which are used to give
authorization to other users.
User ids allow access to SAP applications. Each user must have a corresponding profile specifically assigned. In many situations, multiple composite profiles can be assigned to a user ID, depending on the roles an individual user is responsible.
Authorizations are the key building blocks of SAP security. Authorization
is the process of assigning values to fields present in authorization objects.
In SAP, access to all system functionality is achieved through a complex array
of authorizations. Sometimes users find that they lack the necessary
authorizations to perform a certain function in the system, in which case the
message: “You are not authorized…” is displayed at the bottom of the screen
A Profile Generator PFCG is
used to automatically generate and assign authorization profiles. The administrator can also create
authorization profiles manually.
Default User ids:
· User Ids Client Name
· SAP* 000 and 001
· DDIC 000 and 001
· Early Watch 066
A user Administration must be similar with the tasks and responsibilities
of admin for creation, managing and controlling access to the R/3
system and its data, and also various R/3 user types and its
data.
Must manage and create new user, groups and profiles using R/3
transaction.
Be similar Authorizations are the key building blocks of SAP
security. Authorization is the process of assigning values to fields present in
authorization objects. With monitoring active users.
Transport client specific user objects between R/3 system or
Clients.
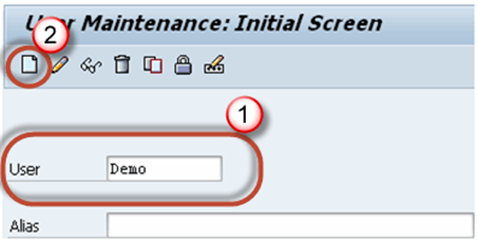
SU01: How to Create a New User in SAP
Step 1) Execute T-code SU01
Step 2)
1.
Enter Username which
you want to create.
2.
Click the create button
Step 3) in the next screen
1.
Click the Address tab.
2.
Enter Details
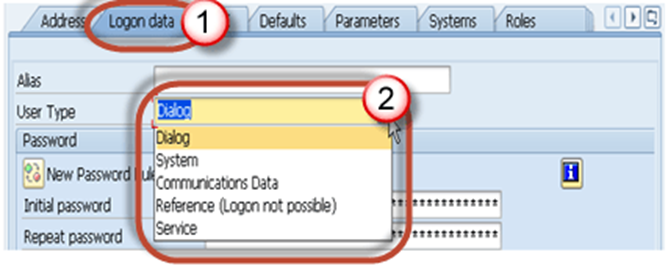
Step4) Choose the user type in Logon Data tab.
There are 5 types of users in sap:-
1.
Dialog user: - Normally it is used
for interactive system access from GUI (used for human users)
2.
System user: - Normally it is used for Background processing, communication
within a system.
3.
Communication user: - It is used for external RFC
calls.
4.
Service user: - Dialog user available to a larger, anonymous group
of users.
5.
Reference user: - General, non-person related users that allows the
assignment of additional authorizations. Example, Internet users created with
transaction SU01. No logon is
possible.
Step 5) Type the initial password for 2
times.
On first logon of the new user, system will ask to re-set the password.
Step 6)
1.
Select the roles tab
2.
Assign roles as per requirements
Step 7)
1.
Select the profiles tab
2.
Assign profiles as per requirements
You can
assign SAP_ALL and SAP_New profile to
user for full authorization.
·
SAP_ALL: You assign this profile to users who are to have all R/3
authorizations, including super-user authorization.
·
SAP_NEW: You assign this profile to users who have access to all
currently unprotected components. The SAP_NEW profile grants unrestricted
access to all existing functions for which additional authorization checks have
been introduced. Users can therefore continue to work uninterrupted with
functions which are subject to new authorization checks which were not
previously executed.
Step 8)
1.
Press save
2.
Then the back button (F3) button
User will be created!
How
to Lock (SU01) & Unlock (SU10) a SAP User
Locking a user
The Purpose of locking user is to temporarily
deactivate the users so that they cannot longer access the system.
Users can be locked in 2 ways:-
·
Automatically
·
Explicitly/Forcefully
Automatically: - There are two
possibilities when users get lock automatically
· Maximum number of failed
attempts: - controlled via the parameter login/fails_to_user_lock. If
a value is set to 3 it means after 3 failed attempts user will be locked.
· Auto unlock time: - "login/failed_user_auto_unlock"
defines whether user locked due to unsuccessful logon attempts should be
automatically removed at midnight.
Explicitly/Forcefully: We can lock and unlock
users in 2 ways-
1.
Lock single user (SU01)
2.
Lock multiple user (SU10)
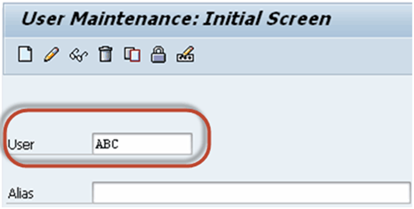
Procedure to lock a single user
Step 1) Execute T-code SU01
Step 2) Enter a username in User field.
Step 3) Press Lock/Unlock button
Step 4) in the next screen, Press Lock button again to lock the user.
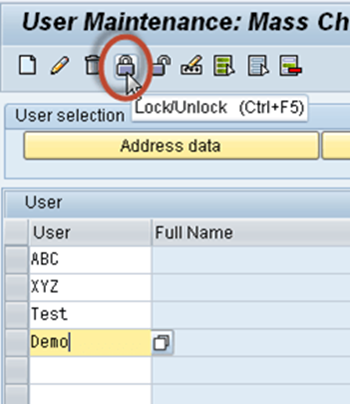
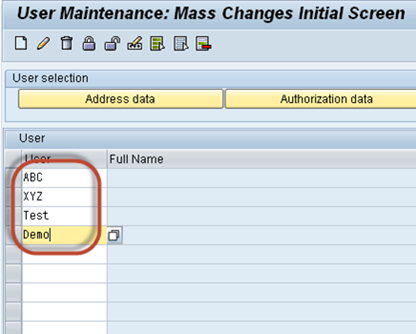
Procedure to lock multiple users
Step 1) Execute T-code SU10
Step 2) Enter users a username in User field.
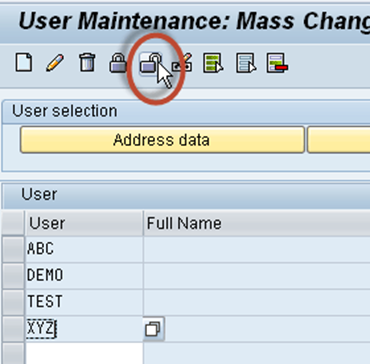
Step 3) Press Lock/Unlock button
All the users listed will be locked
Procedure to unlock a user
Step 1) Execute T-code su01
Step 2) Enter username in User field.
Step 3) Press Lock/Unlock button
Step 4) Press Unlock button
Procedure to unlock multiple users
Step 1) Execute T-code SU10
Step 2) Enter users' username in User field.
Step 3) Press Unlock button
Users will be unlocked
SAP RZ11: Parameter
(login/fails_to_session_end) Limit Logon Attempts
What is a parameter?
Parameter is the set of keys and values to manage the SAP system.
There are two types of parameters -
1.
Static: - It needs a restart. It doesn't effect to the system immediately
once you set the value for it.
2.
Dynamic: - It does not need restart. It effects to the system
immediately once you set the value for it.
How to view
a parameter?
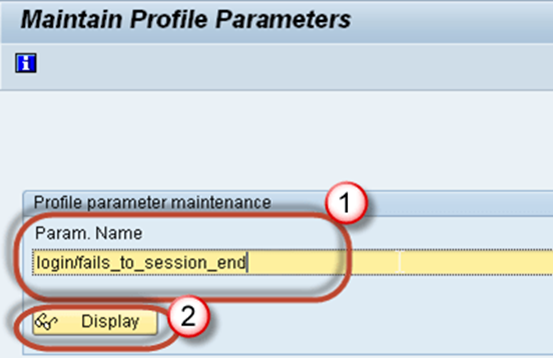
Step 1) Execute T-code RZ11.
Step 2)
1. Put parameter name "login/fails_to_session_end" in
text-field. You can put any Parameter name.
2. Click Display
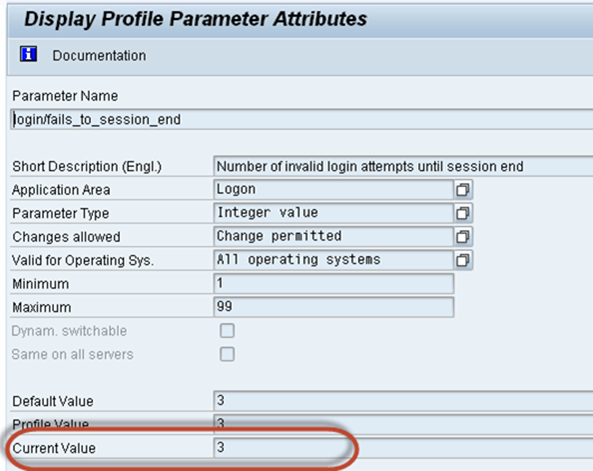
Step 3) the screen below shows the current value set for the parameter by the admin
In order to change a parameter, click the pencil icon
and make desired changes
Important Parameters to limit login
attempts
·
Login/fails_to_session_end: This parameter specifies the
number of times that a user can enter an incorrect password before the system
ends the logon attempt. The parameter is to be set to a value lower than the
value of parameter
·
Login/fails_to_user_lock: This parameter specifies the number
of times that a user can enter an incorrect password before the system locks
the user against further logon attempts. Default value is 12. You can set it to
any value between 1 and 99 inclusive.
SAP USR40: How to set Password
Restrictions
You can use the following system profile parameters to
specify the minimum length of a password and the frequency with which users
must change their password.
·
login/min_password_lng: minimum password length.
Default value: Three
characters. You can set it to any value between 3 and 8.
·
login/password_expiration_time: number of days after
which a password expires
To allow users to keep their passwords without limit,
leave the value set to the default 0.
Specifying
Impermissible Passwords
You can prevent users from choosing passwords that you
do not want to allow. To prohibit the use of a password, enter it in table
USR40. You can maintain table USR40 with Transaction SM30. In USR40,
you can specify impermissible passwords generically if you want. There are two
wildcard characters:
1.
? stands for a single character
2.
* stands for a sequence of any combination characters of
any length.
123* in table USR40
prohibits any password that begins with the sequence "123."
*123* prohibits any password that contains the sequence
"123."
AB? Prohibits all passwords that begin with "AB" and have
one additional character: "ABA", "ABB", "ABC" and
so on.
To set restriction for password follow the below procedure:-
Step 1) Execute T-code SM30.
Step 2) Enter the table name USR40
in "Table/View" field.
Step 3) Click Display
button.
Step 4) Enter password expression
string.
That's it for password management!




















0 Comments
Post a Comment