An application runs in an SAP work process where an ABAP program
is normally executed. The process requires memory to do this, which is
allocated to it by the memory management system. The order in which the work
process is assigned the memory type depends on the work process type, either
dialog or non-dialog (see SAP Memory Types), and the underlying operating
system. This is described in more detail in the documentation on the operating
system.
The SAP Roll Area is used for the initial memory assigned
to a user context, and (if available) for additional memory if the expanded
memory is full.
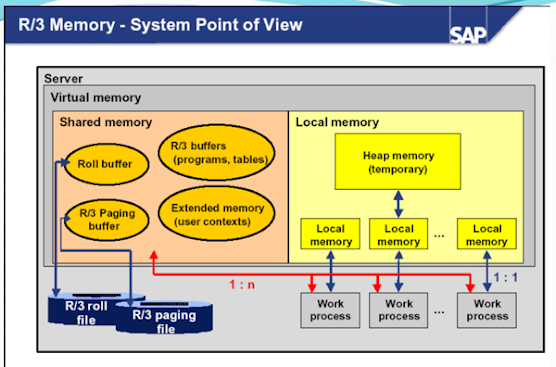
The following diagram displays the memory types that can be assigned to work processes on the SAP and operating system level. Here are the most important system profile parameters that control the availability of the memory types.
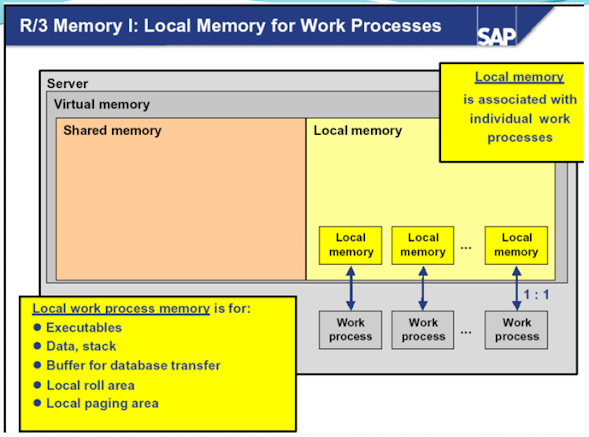
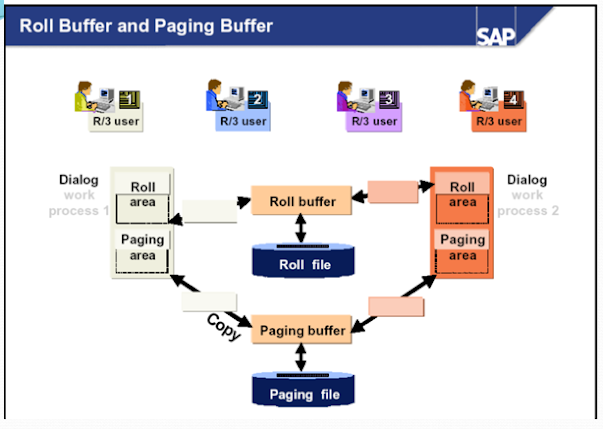
SAP Roll Area
Roll area is
memory area which is allocated by work processes for the program instance.
Each time a user starts a program, a roll area is created for that instance of
the program. It contains the following information about the program's execution:
- the dynamic memory allocations
- variables value
- the current pointer of the program
The roll area
consists of 2 segments. The first segment, which can be set with the parameter
ztta/roll_first, is assigned to the work process first as memory. If this is
used up, the work process has more memory assigned to it. The amount of memory
is determined by the difference between the parameters ztta/roll_area and
ztta/roll_first.
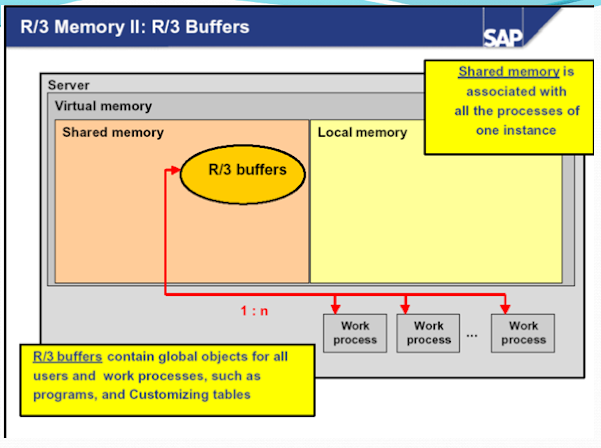
SAP Extended Memory
SAP extended
memory is the core of the SAP memory management system. Each SAP work process
has a part reserved in its virtual address space for extended memory.
You can set the
size of extended memory using the profile parameter em/initial_size_MB:
Extended Memory Pool Size. Configurable under Windows, further memory is
assigned dynamically as needed, and you can also set this amount.
The SAP system
builds a layer onto the operating system functions for the page management of
this memory. This extended memory is implemented as an unnamed mapped file.
This means the address space uses the paging file or uses the swap space of the
operating system as background memory.
Private Memory or Heep Memory
Other processes cannot use private (heap) memory. After releasing the assigned memory, the operating system still considers the (virtual) memory as being occupied by the allocating process. These characteristics of heap memory require that:
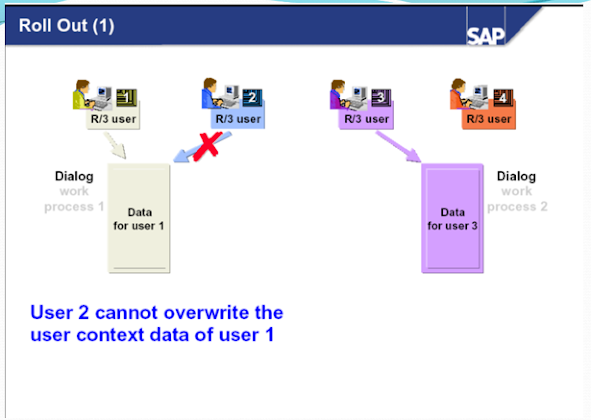
The work process can be run in PRIV mode (private) when the local memory is assigned. This means that the work process is reserved for processing the current user context until the context releases the work process again when the request has ended.
Memory Parameters-:
- ztta/roll_first
= 20KB
- ztta/roll_area
= 1MB
- ztta/roll_extension
= 2GB
- abap/heaplimit
= 8GB
- abap/heap_area_dia
= 4GB
- abap/heap_area_nondia
= 4GB
Memory Management
Memory Allocation
Memory
allocation sequence to dialog work processes in SAP. This article answers the
following questions-:
- What is the memory allocation
sequence to dialog work processes in SAP?
- When does a work process go to PRIV
mode?
- How to avoid or minimize the work process going to PRIV mode?
- What are the SAP parameters used to define initial roll area, extended memory, heap memory?
Memory
allocation sequence to Dialog work process in SAP
- Initially, a defined roll area is used. This roll area is defined by the SAP parameter “ztta/roll_first.”
Usually
ztta/roll_first is set to 1 in SAP, so that only a technically necessary
amount is allocated to roll memory. If the memory from the initial roll area
[ztta/roll_first] is not sufficient for the user context then,
2. Extended memory is used until the extended memory is full or until the user
quota is reached.
Extended memory
is defined by the SAP parameter “em/initial_size_MB” and the user quota for the dialog work process is defined by the parameter “ztta/roll_extension_dia”. If
this memory is not sufficient then,
3. The rest of the roll area is used. This roll area is defined by SAP
parameter “ztta/roll_area _ ztta/roll_first”
4. The system is forced to use local heap memory [private memory]. Then the
work process goes into PRIV mode.













0 Comments
Post a Comment